When talking about collagen, you must first think of skin, right? Actually, collagen is not only important for appearance. Around 30% of the protein in our body is collagen. Collagen is in different parts and systems of the body, providing connection, protection, filtration and strength. It is the substance that plays an important role in connecting the whole body together.
Depending on the type of collagen and the degree of mineralization, collagen may be hard (bone) or soft (tendon) or somewhere in between (cartilage). Nearly 30 different types of collagen are known, some protecting our internal organs like sausage casings and others making our vocal cords sound like the strings of musical instruments. Other places where collagen is needed include: teeth, muscles, arteries, veins, cell membranes, eyes, hair, nails, the mesh tissue that wraps around organs, placental tissue, and more….
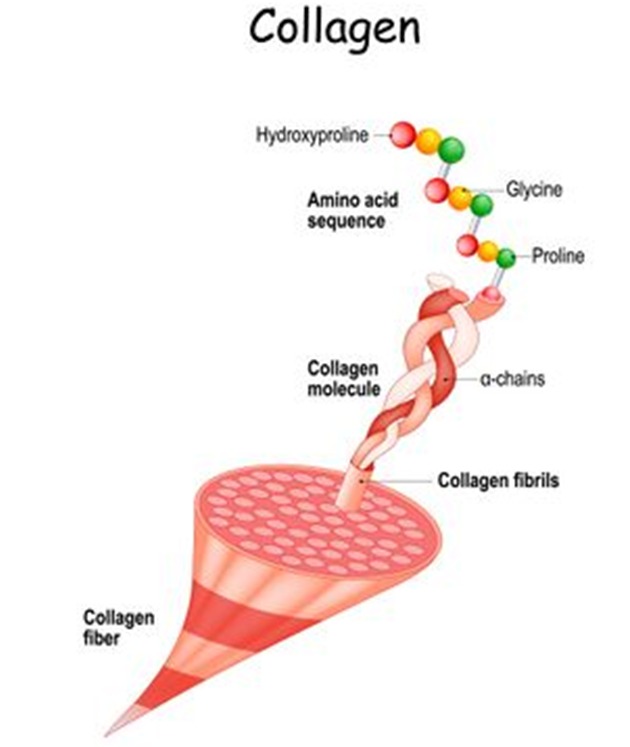
▶ triple helix of glycine, proline and hydroxyproline, intertwined with each other
▶ Strength can be stronger than steel
▶ Not only in the form of single long cords, but also in striated horizontal sheets (e.g. retina)
Age is Collagen’s Worst Enemy With age
♦ Collagen produced by the body will decrease
♦ Existing collagen will break down at a faster rate
♦ The quality of collagen is also lower than before
♦ Significant reduction in collagen production in postmenopausal women
♦ Collagen production declines for everyone after age 60
This can lead to not only wrinkled skin, but also brittle blood vessels, sagging organs, deteriorated vision, etc., etc.
Where does collagen come from
📌 Collagen cannot be absorbed by the body in its intact form
📌 The body will break down the collagen it eats into amino acids, & with other substances together, produce different types of collagens in different parts of the body.
📌 Therefore, eating collagen-rich foods alone will not directly lead to increased collagen levels in the body.
📌 Many foods that provide raw materials that support collagen production can be part of a healthy diet.
📌 These foods contain amino acids: proline and glycine.
📌 The process also requires vitamins A, C, anthocyanins, zinc and copper.
Supplementation of raw materials is only part of the story:
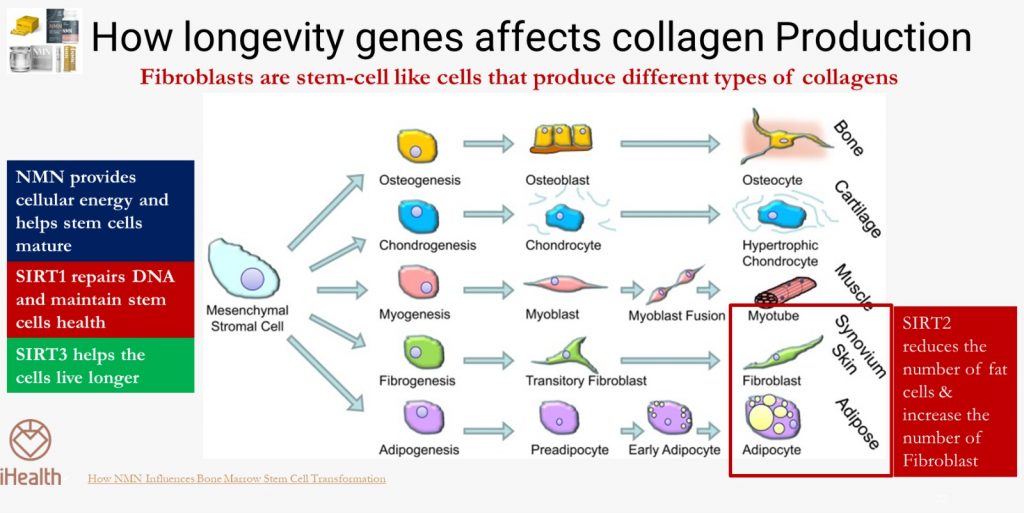
To produce high-quality collagen, the body needs fibroblast cells (which are derived from mesenchymal stem cells) in the works.
But did you know that as we get older, not only does the number of mesenchymal stem cells decrease, but the proportion of mesenchymal stem cells that differentiate into fat cells also increases significantly, so that the proportion of mesenchymal stem cells that differentiate into other cells, including fibroblasts, decreases significantly?
So even if there are raw materials, they may not be of much use, because there maybe insufficient machines to produce the required collagen.
The good news is that NMN can provide cellular energy, and can activate all seven longevity genes (SIRT1 – 7)*, which can increase the number of mesenchymal stem cells. Among the 7 longevity genes, SIRT1 after being activated, can monitor the production of fat cells (Adipose) like when you were young. SIRT1 can repair DNA. The 2 *working together, can directly increase the number and quality of fibroblasts, and quickly resume the production of different collagens that are needed in the body.
Therefore, a lot of NMN users reported that they have experience improved vision, improved skin, darkened hair, no more incontinence, knee pain, back pain, … and so on!
https://www.nmn.com/news/nmn-stimulates-bone-marrow-stem-cells
