There is a huge web of nerves in our guts. A nerve is a bundle of neurons.
By analyzing gene activity in these individual neurons, the scientists infer that neurons in the gut are communicating with a variety of other cell types, including immune cells. They also found that key genes associated with disease are expressed in these cells.
The Brain-Gut Connection
https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/wellness-and-prevention/the-brain-gut-connection
The *enteric nervous system (ENS)*…. is two thin layers of more than 100 million nerve cells lining your gastrointestinal tract from esophagus to rectum.
Unlike the big brain in your skull, the ENS can’t balance your checkbook or compose a love note. “Its main role is controlling digestion, from swallowing to the release of enzymes that break down food to the control of blood flow that helps with nutrient absorption to elimination,”
“The enteric nervous system doesn’t seem capable of thought as we know it, but it communicates back and forth with our big brain—with profound results.”

https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Enteric_nervous_system
The enteric nervous system (ENS) is considered semi-autonomous because it can function independently of the central nervous system. The ENS has a network of two-way connections with the central nervous system, but it can act autonomously rather than rely on signals from the central nervous system. The ENS has as many neurons as the spinal cord, which is why some experts describe it as part of the overall nervous system instead of the autonomic nervous system. The ENS has been referred to as a second brain because of its extent and degree of autonomy.
Health of the enteric nervous system is of no less importance than the other elements of gut health.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-1215119597-543e3e83a27248609e42c240f1c7ad68.jpg)
What are the symptoms of enteric nervous system dysfunction?
ENS dysfunction can be associated with a number of GI symptoms including severe constipation, anorexia, and delayed gastric emptying (gastroparesis), which are all common in patients with neurodegenerative conditions.
Mayo Clinic Study Shows Spinal Cord Nerves Depend on NAD+
…. increasing NAD+ levels, either by blocking the consumption of NAD+ or supplementing with the precursor nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN), attenuated oligodendrocyte loss and promoted myelin regeneration.
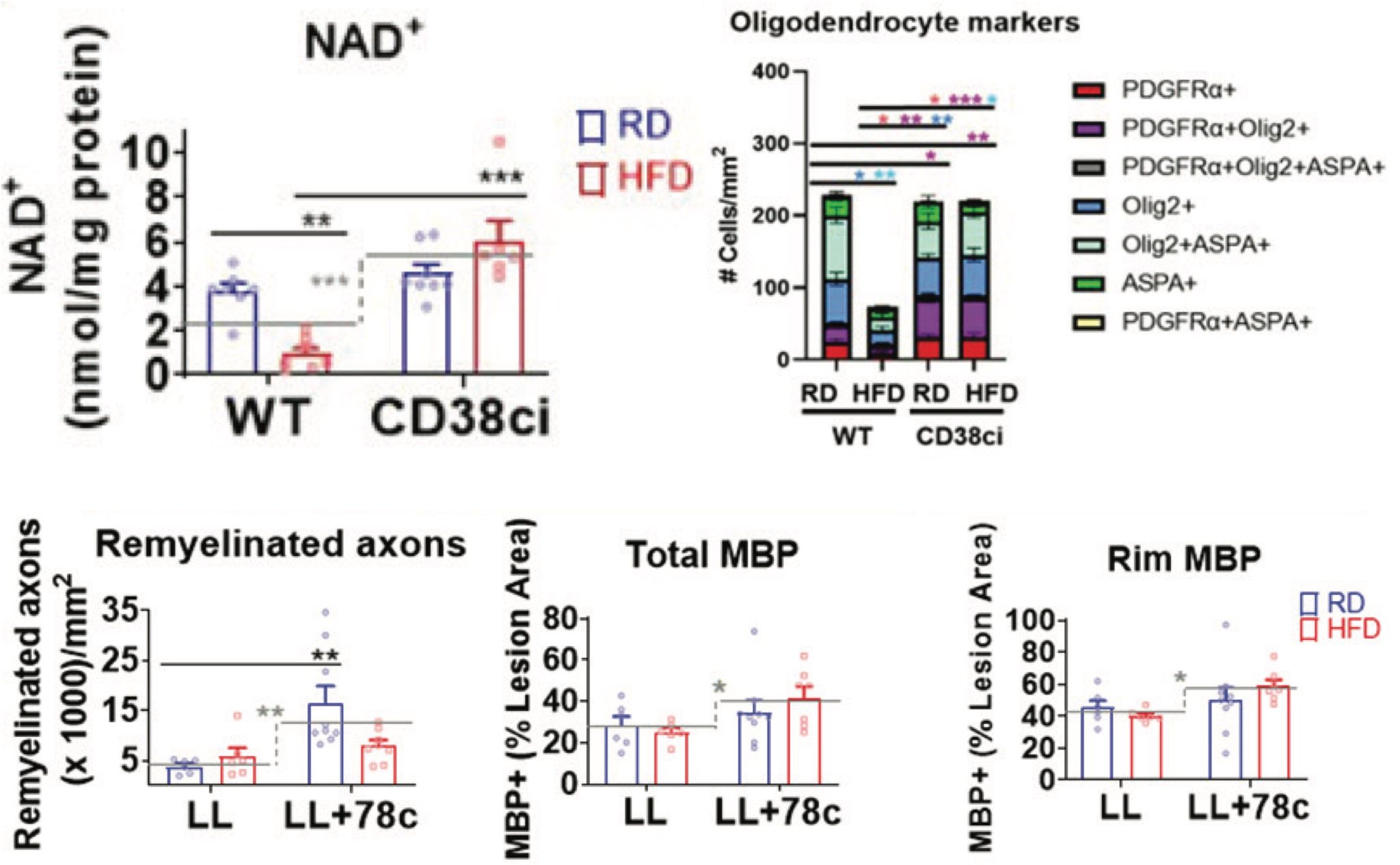
https://www.nmn.com/news/mayo-clinic-spinal-cord-nerve-projection-health-nad
NAD+ Precursors NMN and NR Prevent Nerve Fiber Degradation in Diabetes
https://www.nmn.com/news/nad-nmn-nr-prevent-nerve-fiber-degradation-diabetes
Study Shows NMN Can Protect the Mouse Intestinal Tract by Altering Gut Microbiome Diversity
In a word, NMN can improve gut health with respect to all the different elements namely collagen generation, muscle strength, blood circulation, protection of nerve cells & balancing of microbiomes.
Happy reading. Bye for now!